How do metal welding parts provide high precision and strength to support the stable operation of automated automotive equipment?
Release Time : 2025-12-26
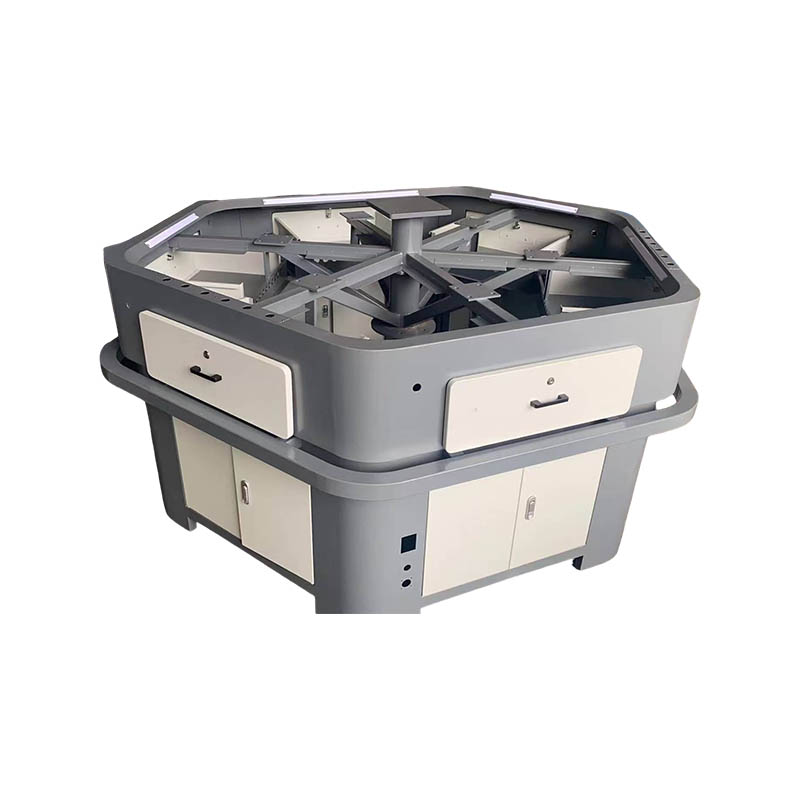
In modern automotive manufacturing plants, automated equipment such as robotic arms, conveyor systems, fixture platforms, and inspection units operate day and night. Behind these systems are thousands of metal welding parts silently undertaking crucial functions such as structural support, power transmission, and precise positioning. These seemingly ordinary steel or aluminum components, through advanced welding processes and rigorous quality control, are endowed with strength, rigidity, and geometric precision far exceeding that of the raw materials themselves, becoming the "industrial backbone" ensuring the high-speed, stable, and long-term operation of the entire production line.
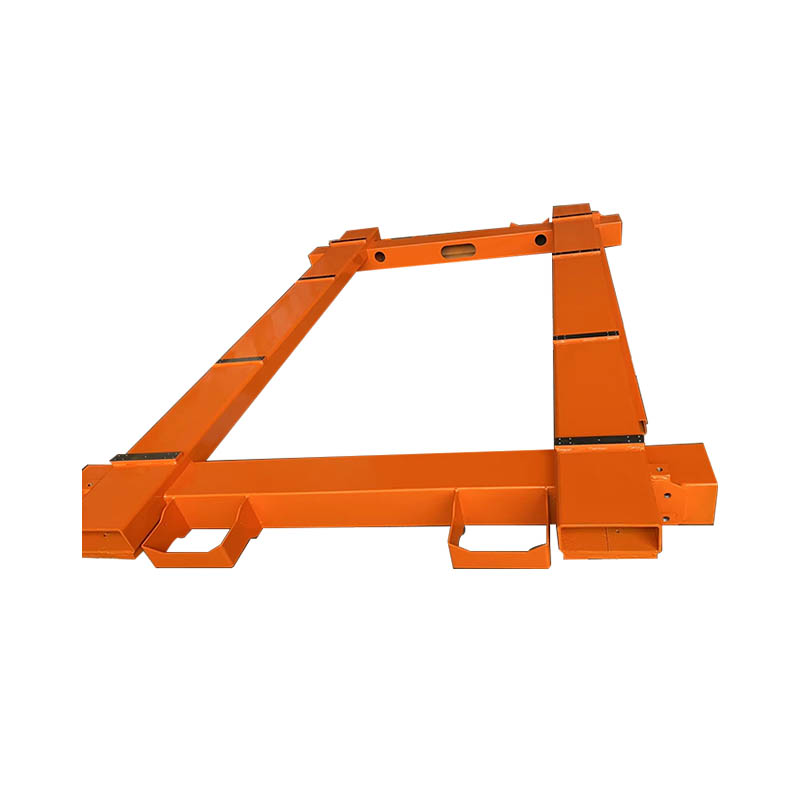
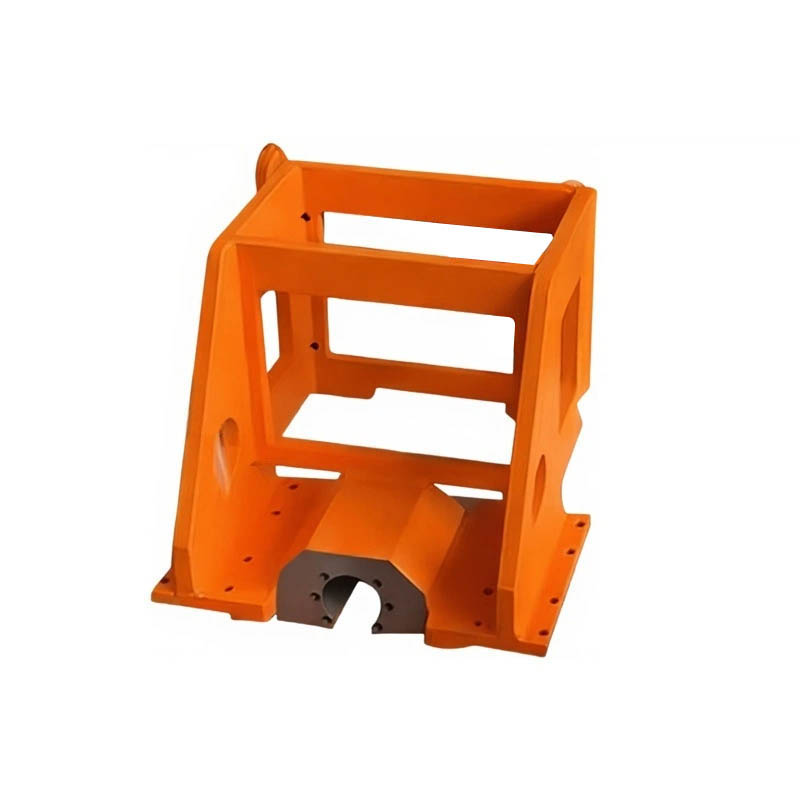
The core advantages of metal welding parts are primarily reflected in their structural integrity and mechanical properties. Employing robotic MIG/MAG, TIG, or laser welding technologies, the weld penetration is uniform, and the heat-affected zone is small, effectively avoiding defects common in traditional manual welding, such as porosity, slag inclusions, or incomplete fusion. Post-weld stress relief treatment significantly reduces the risk of residual deformation, ensuring that large frames or cantilever structures maintain dimensional stability under long-term loads. This high reliability enables welded components to withstand frequent start-stop cycles, high-speed movements, and heavy-duty impacts, providing a solid foundation for automated equipment.
The synergistic optimization of materials and processes in metal welding parts further enhances their applicability. Depending on functional requirements, carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, or aluminum alloy can be selected as the base material, matched with appropriate welding parameters and shielding gases. For example, the load-bearing base uses high-strength low-alloy steel, balancing rigidity and weight reduction; the moving linkage uses tempered steel, achieving excellent fatigue strength after welding and local heat treatment; and the support in clean areas is made of stainless steel, ensuring corrosion resistance and compatibility with cleanroom environments. Each material combination undergoes process verification to ensure dense weld microstructure and satisfactory mechanical properties.
Metal welding parts also excel in geometric accuracy and assembly consistency. Utilizing 3D laser scanning and CNC positioning fixtures, multi-part welding can be completed within millimeter-level tolerances, with highly controllable flatness of key mounting surfaces and coaxiality of holes. This precision ensures seamless integration with subsequent precision components such as servo motors, guide rails, and sensors, preventing equipment vibration, abnormal noise, or positioning misalignment due to accumulated errors. Especially on multi-station synchronous welding lines, the repeatability of the manufacturing precision of welded structural components directly determines the overall vehicle assembly quality.
Modular design principles give metal welding parts both flexibility and maintainability. Large equipment is often assembled from multiple standardized welding units, facilitating transportation, on-site assembly, and future upgrades. Key load-bearing nodes utilize detachable flanges or pin connections; when local wear or damage occurs, only the module needs replacement instead of the entire machine, significantly reducing lifecycle costs. Surface treatments such as sandblasting, phosphating, or powder coating enhance resistance to oil stains and scratches, adapting to complex workshop conditions.
Furthermore, the manufacturing process of metal welding parts incorporates a comprehensive quality control system. From raw material spectral analysis, pre-weld beveling inspection, and welding process parameter recording, to post-weld non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic or penetrant testing) and coordinate measuring machine (CMM) measurements, every step is traceable. Some key components also undergo dynamic load simulation testing to verify their fatigue life under real-world conditions, ensuring "zero-defect" delivery.
When an automated machine precisely picks up a car body in the welding workshop, and when a conveyor platform smoothly transports the body-in-white across the painting line, countless welding parts are working silently behind the scenes. They don't emit light, yet they support the pulse of the smart factory; they are silent, yet they safeguard the manufacturing rhythm with millimeter-level precision. Because in the underlying logic of intelligent automotive manufacturing, true automation not only relies on software algorithms, but is also rooted in those carefully welded and rigorously inspected metal structures—and this is precisely the irreplaceable value of high-quality metal welding parts.
The core advantages of metal welding parts are primarily reflected in their structural integrity and mechanical properties. Employing robotic MIG/MAG, TIG, or laser welding technologies, the weld penetration is uniform, and the heat-affected zone is small, effectively avoiding defects common in traditional manual welding, such as porosity, slag inclusions, or incomplete fusion. Post-weld stress relief treatment significantly reduces the risk of residual deformation, ensuring that large frames or cantilever structures maintain dimensional stability under long-term loads. This high reliability enables welded components to withstand frequent start-stop cycles, high-speed movements, and heavy-duty impacts, providing a solid foundation for automated equipment.
The synergistic optimization of materials and processes in metal welding parts further enhances their applicability. Depending on functional requirements, carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, or aluminum alloy can be selected as the base material, matched with appropriate welding parameters and shielding gases. For example, the load-bearing base uses high-strength low-alloy steel, balancing rigidity and weight reduction; the moving linkage uses tempered steel, achieving excellent fatigue strength after welding and local heat treatment; and the support in clean areas is made of stainless steel, ensuring corrosion resistance and compatibility with cleanroom environments. Each material combination undergoes process verification to ensure dense weld microstructure and satisfactory mechanical properties.
Metal welding parts also excel in geometric accuracy and assembly consistency. Utilizing 3D laser scanning and CNC positioning fixtures, multi-part welding can be completed within millimeter-level tolerances, with highly controllable flatness of key mounting surfaces and coaxiality of holes. This precision ensures seamless integration with subsequent precision components such as servo motors, guide rails, and sensors, preventing equipment vibration, abnormal noise, or positioning misalignment due to accumulated errors. Especially on multi-station synchronous welding lines, the repeatability of the manufacturing precision of welded structural components directly determines the overall vehicle assembly quality.
Modular design principles give metal welding parts both flexibility and maintainability. Large equipment is often assembled from multiple standardized welding units, facilitating transportation, on-site assembly, and future upgrades. Key load-bearing nodes utilize detachable flanges or pin connections; when local wear or damage occurs, only the module needs replacement instead of the entire machine, significantly reducing lifecycle costs. Surface treatments such as sandblasting, phosphating, or powder coating enhance resistance to oil stains and scratches, adapting to complex workshop conditions.
Furthermore, the manufacturing process of metal welding parts incorporates a comprehensive quality control system. From raw material spectral analysis, pre-weld beveling inspection, and welding process parameter recording, to post-weld non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic or penetrant testing) and coordinate measuring machine (CMM) measurements, every step is traceable. Some key components also undergo dynamic load simulation testing to verify their fatigue life under real-world conditions, ensuring "zero-defect" delivery.
When an automated machine precisely picks up a car body in the welding workshop, and when a conveyor platform smoothly transports the body-in-white across the painting line, countless welding parts are working silently behind the scenes. They don't emit light, yet they support the pulse of the smart factory; they are silent, yet they safeguard the manufacturing rhythm with millimeter-level precision. Because in the underlying logic of intelligent automotive manufacturing, true automation not only relies on software algorithms, but is also rooted in those carefully welded and rigorously inspected metal structures—and this is precisely the irreplaceable value of high-quality metal welding parts.